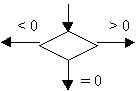![]()
Quality Tools > Flowcharting
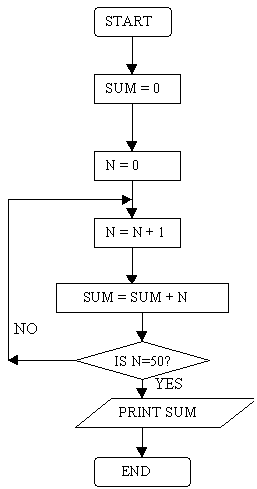
Flowcharting is a tool for analysing processes. It allows the team to break any process down into individual events or activities showing the logical relationships.
Flowcharting is a simple way of creating a visual representation of sequence of activities.
Constructing flowcharts promotes better understanding of processes, which is a prerequisite for improvement.
Need for a flowchart in an organisation:
An organisation consists of many interrelated operations. These are sometimes complicated and seldom modified in response to customer requirements, laws and regulations. Top management often make modifications in the processes without considering the other employees. This is not conducive to the organization.
The best alternative would be to categorize the responsibilities into areas of activities and share the needs of the organisation with the other workforce. The next step would be to prepare flowcharts of the stages in each process so that the employees can get a clear picture of the process flow. The flowcharting technique helps one to move in the right direction, gather critical information, and correlate various processes.
There are three types of flow charts.
- The high level flow chart.
- Matrix flow chart.
- Detailed flow chart.
High-level flow diagram visually represents the sequence of activities in a process without detailing them.
A matrix flow chart consists of relating the activities to unique entities in the organisation.
A detailed flow diagram takes into account the plausible problems in the process and the course of action to be followed once there is a problem.
Guidelines for preparing a flowchart:
Flowcharts are generally represented using standard symbols. Some standard symbols, commonly needed for flowcharting are: